
Conducting Audience Analysis

Introduction to Audience Analysis
Conducting audience analysis is a fundamental step in any form of communication, especially in visual communication for posters. Whether it's academic, corporate, or informal settings, audience analysis helps tailor messages to resonate on a deeper level. Understanding who the audience is—their preferences, challenges, and expectations—enables creators, speakers, and marketers to craft messages that are not only received but also appreciated and acted upon. Whether it’s about deciding how to craft research poster narratives or choosing the right design for a public speaking for posters event, success hinges on how well the audience is understood.
The Importance of Background Information
Audience analysis has evolved with digital media and diverse global audiences. This includes understanding demographic data, psychographic profiles, and the contextual circumstances of the audience. The tools for analyzing an audience range from surveys and interviews to digital analytics. When considering engaging visuals for posters, understanding the academic audience requires different strategies than engaging a corporate or mixed demographic. For example, the visual aid design for posters aimed at business professionals would focus on clarity and professionalism, while posters for a broader demographic might use more vibrant and accessible designs.
Referencing External Sources
Studies validate the importance of thorough audience analysis. According to a survey by the Content Marketing Institute, 72% of marketers saw an increase in engagement through targeted content creation based on audience analysis. Another study highlighted by the Harvard Business Review shows that companies engaging in comprehensive audience analysis outperform their competitors in customer loyalty and revenue growth. This highlights how critical audience understanding is for projects like creating visual communication for posters, where every design element should align with the audience's needs and expectations.
Discover How INK PPT Can Elevate Your Presentation Design
Tailoring Your Message to Audience Needs

Introduction to Tailoring Your Message
The essence of tailoring your message lies in the ability to adapt your communication to fit the specific needs, interests, expectations, and context of your audience. This personalized approach ensures that your message is not just heard but is meaningful to those who receive it. Whether crafting a visual aid design for posters or an informative business presentation, Whether it’s crafting a compelling business presentation, designing an informative poster, or preparing educational presentation slides, the effectiveness of your message is significantly enhanced when it speaks directly to the audience’s needs.
Background and Key Considerations
The concept of message tailoring is rooted in the field of audience research and psychology, drawing from principles that understand the audience not as a monolithic group but as individuals with unique preferences and behaviors. Key considerations in this process include language use, cultural sensitivities, emotional appeals, and the clarity of the call to action. For instance, engaging visuals for posters designed for a corporate audience might prioritize professionalism and data-driven insights, while a craft research poster narrative for academic use would require more focus on clarity and factual accuracy.
Illustrations from Real-World Scenarios
Examples of successfully tailored messages abound in the marketing and educational fields. A notable case is how non-profit organizations tailor their fundraising messages to different segments of their audience, using emotional storytelling for general public campaigns, while presenting detailed impact reports and financials to institutional donors. In an academic setting, educators might use a variety of presentation examples and multimedia elements to cater to the diverse learning styles of their students, making the learning experience more engaging and effective.
Support from External Research
Research supports the effectiveness of message tailoring. A study published in the Journal of Communication found that tailored health messages were significantly more effective in changing behavior than generic messages. Another example is a business report by Forbes, highlighting how companies using customer data to tailor marketing messages see an increase in engagement rates by up to 8 times. These insights not only validate the importance of tailoring your message but also showcase the tangible benefits of this approach in real-world applications.
Tailoring your message to meet audience needs is not just about altering surface elements; it’s about deep engagement with your audience’s worldview and crafting your communication to resonate on a personal level. This section has explored the ideas and nuances of message tailoring and provided a framework for thinking about communication as a customizable tool designed to meet specific audience needs.
Explore Our Case Studies for Real-World Impact
Understanding the Academic Audience

Introduction to Academic Audiences
Engaging an academic audience requires a strategic approach that respects the intellectual rigor and critical mindset inherent to this group. Whether presenting at a conference, publishing research findings, or creating academic posters, the content must be underpinned by thorough research, clear argumentation, and a well-structured presentation. Understanding this audience's expectations is key to crafting messages that inform, persuade, and engage at the highest level of scholarly communication.
Background and Contextual Understanding
Academic audiences often seek depth, precision, and innovation in the content they consume. They value information that contributes meaningfully to existing bodies of knowledge, offers fresh perspectives, or challenges conventional thinking. The historical context of academic discourse, rooted in the principles of critical inquiry and evidence-based argument, shapes how messages are received and interpreted. This background highlights the importance of not just what is communicated but how it's substantiated and presented.
Real-World Examples and Application
A prime example of successful engagement with academic audiences can be seen in how researchers tailor their presentation slides for scholarly conferences. These slides often prioritize clarity, focus on key findings, and anticipate critical questions. Another instance is the use of video presentations in online education, where instructors blend academic rigor with visual storytelling to enhance learning outcomes. Poster sessions at academic conferences also illustrate the need for visually appealing yet informative poster session designs that can communicate complex research in an accessible and engaging manner.
Evidence from Studies and Reports
Research underscores the effectiveness of these approaches. A study in the "Journal of Educational Psychology" demonstrated that academic audiences are more likely to engage with content that employs clear, concise language and includes visual aids to illustrate complex ideas. Furthermore, a report by the Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education found that academic presentations incorporating interactive elements like Q&A sessions or live polls significantly increase audience engagement and retention of information.
Understanding and engaging an academic audience is a nuanced process that requires a careful balance of depth, clarity, and engagement. This section has shed light on the unique characteristics of academic audiences and provided guidance on how to effectively communicate with this group, ensuring that your message is not only heard but valued.
Engaging a Corporate Audience

Introduction to Corporate Audiences
Engaging a corporate audience demands an understanding of the business context, including the market dynamics, company culture, and the specific goals of the presentation or communication effort. Whether it’s a pitch for a new project, a business presentation to stakeholders, or a workshop for skill development, the message needs to be clear, persuasive, and directly relevant to the business objectives at hand. This requires not only a firm grasp of the subject matter but also the ability to convey it in a manner that resonates with business professionals.
Background and Strategic Approach
The key to engaging a corporate audience lies in the strategic alignment of the message with the business's goals and the audience's roles within the organization. This involves an analysis of the business model, the competitive landscape, and the professional backgrounds of the audience members. Effective communication in this context often leverages business presentation templates that are structured to highlight key points, data-driven insights, and clear calls to action. The background and context provided shape the delivery, presentation example and design of the message, ensuring it is both impactful and actionable.
Illustrations from the Business World
Real-world examples of successful engagement with corporate audiences include the use of compelling interactive presentation slides in quarterly earnings calls, where complex financial data is distilled into understandable insights for investors and analysts. Another example is the strategic use of video presentations in online marketing campaigns, where businesses articulate their value proposition through engaging stories that connect with their target audience's needs and aspirations. Moreover, interactive presentations during corporate training sessions can significantly enhance learning and retention by actively involving participants in the learning process.
Supporting Evidence and Case Studies
Research and case studies further highlight the importance of tailored communications for corporate audiences. For instance, a Harvard Business Review article emphasized the effectiveness of storytelling in business presentations, noting that narratives that connect on an emotional level can significantly enhance audience engagement and persuasion. Additionally, a study in the Journal of Business Communication found that presentations utilizing a combination of visual and verbal elements were more effective in influencing audience decisions, underscoring the value of well-designed slides and visual aids in corporate settings.
Engaging a corporate audience requires a careful blend of business acumen, strategic messaging, and compelling presentation techniques. This section has explored the nuances of corporate communication, offering insights into how to craft messages that resonate with business professionals and drive meaningful action.
Strategies for a Mixed Audience
Introduction to Mixed Audience Engagement
Engaging a mixed audience requires a nuanced understanding of its composition and the common ground that unites different members. Whether it’s a public speaking event, an educational workshop, or a marketing campaign, the goal is to deliver a message that is relevant and engaging to everyone in the audience. This involves a careful balance of complexity and simplicity, specialization and generality, ensuring that the content is neither too elementary for experts nor too complex for novices.
Background and Considerations for Diversity
A mixed audience can vary not only in terms of expertise but also in cultural backgrounds, age groups, and personal interests. Effective communication in this context demands an awareness of these diversities and a strategic approach to message design. This includes using clear and inclusive language, avoiding jargon, and incorporating diverse presentation examples and visual elements that cater to different learning styles and preferences. Understanding the varied dynamics of a mixed audience sets the stage for crafting messages that are broadly accessible and impactful.
Illustrations from Varied Contexts
Real-world scenarios where strategies for mixed audiences are effectively employed include community town hall meetings, where speakers address a wide demographic range, and product launches, where companies aim to appeal to both existing customers and new prospects. Educational webinars and seminars also illustrate the need for adaptable content delivery, where information must be made relevant and engaging for attendees with varying levels of familiarity with the topic. These examples highlight the importance of flexibility, inclusivity, and creativity in engaging mixed audiences.
Evidence from Research and Analysis
Research supports the effectiveness of adaptive communication strategies for mixed audiences. A study in the "International Journal of Business Communication" found that messages tailored to address the diverse needs and preferences of a mixed audience resulted in higher levels of engagement and satisfaction among participants. Furthermore, an analysis published in the "Journal of Marketing Communications" demonstrated that incorporating multimedia elements and interactive sessions in presentations significantly enhances comprehension and retention across varied audience segments.
Engaging a mixed audience effectively requires a strategic blend of clarity, inclusivity, and adaptability. By understanding the diverse needs and preferences of the audience, communicators can craft messages that are both accessible and engaging to everyone, regardless of their background or expertise level. This section has provided insights into the challenges and strategies for successfully communicating with a mixed audience, offering practical advice for achieving broad engagement.
Age Demographics and Content Adaptation
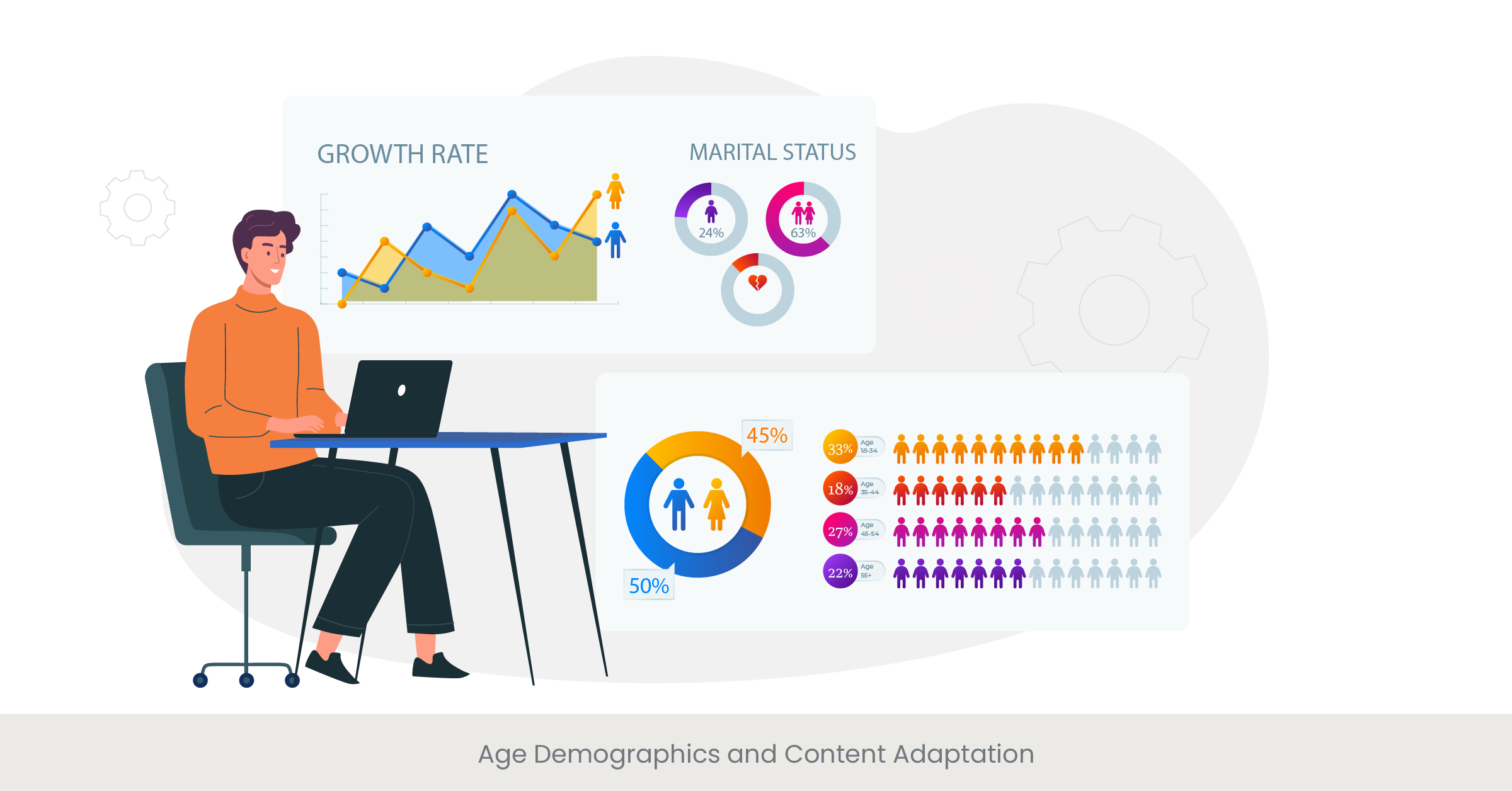
Introduction to Age-Based Content Strategy
Understanding and adapting content to cater to different age demographics is essential for communicators, educators, and marketers alike. From designing a presentation for a diverse audience to creating educational materials for different age groups, the approach must consider the audience's age-specific interests, learning styles, and digital literacy. Tailoring content to age demographics not only enhances engagement but also maximizes the impact of the message being delivered.
Background and Generational Preferences
Each age group or generation brings its own set of preferences, cultural touchstones, and technological comfort levels. For instance, while digital natives like Millennials and Gen Zers might prefer interactive presentations and video content, older generations such as Baby Boomers and Gen Xers may appreciate more traditional, text-based communication and detailed presentation slides. Understanding these generational differences is key to developing a communication strategy that effectively resonates with each segment.
Real-World Examples and Approaches
In practice, adapting content for various age demographics can be seen in how educational institutions use technology to engage younger students through gamification and interactive learning platforms, while adult education often focuses on practical applications and direct relevance to professional or personal development. Marketing campaigns, too, demonstrate this adaptation, with brands using social media and influencer partnerships to reach younger audiences, while traditional media channels like television and print are used to engage older demographics. These examples illustrate the importance of selecting the right medium and message style for each age group.
Supporting Evidence and Research
Research underscores the importance of age-specific content adaptation. A study published in the "Journal of Educational Psychology" found that younger students showed significantly higher engagement and retention rates with multimedia and interactive content compared to traditional lecture formats. Conversely, a survey conducted by the Pew Research Center revealed that older adults prefer detailed articles and reports, valuing depth and thoughtfulness over the brevity often favored by younger readers. These findings highlight the necessity of understanding and addressing the unique preferences of different age groups to optimize communication effectiveness.
Adapting content to meet the needs of various age demographics is not just about changing the medium or simplifying the message; it's about understanding the unique perspectives, values, and experiences that each generation brings to the table. This approach ensures that messages are not only received but are also meaningful and engaging to diverse audiences, regardless of their age.
Cultural Considerations in Poster Design

Introduction to Cultural Sensitivity in Design
Creating a poster that is culturally sensitive and appealing requires more than just an eye for visual communication for posters; it demands an understanding of the cultural norms, values, and symbols of the target audience. Whether it’s for an academic conference, a business event, or a social campaign, the design must navigate cultural nuances to ensure the message is received as intended, without causing offense or misunderstanding. This entails a thoughtful selection of images, colors, typography, and content that aligns with the cultural context of the audience, enhancing both the visual communication for posters and the message being conveyed.
Background on Cultural Diversity and Design
Cultural diversity encompasses a wide range of elements, including language, religious beliefs, societal norms, visual hierarchy, and aesthetic preferences. For example, crafting research poster narratives requires careful attention to color symbolism, which varies significantly between cultures, with white symbolizing purity in some contexts and mourning in others. Similarly, certain imagery and icons may carry positive connotations in one culture and negative in another. Understanding these cultural factors is essential for creating posters and visual materials that are both respectful and effective, ensuring the visual communication for posters is culturally appropriate.
Enhance Your Visual Storytelling with INK PPT
Evidence from Studies and Design Principles
Research in the field of intercultural communication and design highlights the impact of culturally adapted visuals on audience engagement and message effectiveness. A study published in the "Journal of Global Marketing" showed that advertisements tailored to cultural preferences significantly outperformed generic ads in terms of audience attention and brand recall. Additionally, design guidelines from the International Institute for Information Design emphasize the role of cultural awareness in creating effective and inclusive visual communications. When crafting research poster narratives, it's crucial to integrate these insights to make the content relatable to diverse audiences.
Incorporating cultural considerations into poster design is not just about avoiding faux pas; it’s about forging deeper connections with the audience by acknowledging and respecting their cultural background. This approach not only enhances the engaging visuals for posters but also ensures that the message is conveyed in a manner that is meaningful and respectful to the audience’s cultural context.
The Importance of Accessibility
Introduction to Accessibility in Communication
Accessibility is about designing your communications—whether it’s a video presentation, a poster, or digital content—so that everyone, including people with disabilities, can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with your work. This is particularly important in visual communication for posters, where accessibility can determine whether or not your audience can fully engage with the content. Emphasizing accessibility not only reflects a commitment to inclusivity but also expands your message's reach, ensuring it is heard and understood by a diverse audience.
Background and Key Principles
The principles of accessible design are guided by the understanding that users have a diverse range of hearing, movement, sight, and cognitive abilities. For example, when crafting research poster narratives or creating engaging visuals for posters, it's important to implement accessibility measures such as alternative text for images, readable fonts, and color contrast adjustments. These principles are not just ethical considerations; they are also legal requirements in many jurisdictions, underscoring the importance of incorporating accessibility into all stages of poster and visual aid design for posters.
Supporting Evidence and Research
Research underscores the effectiveness of accessible design in broadening audience engagement. A study published in the Journal of Accessibility and Design for All found that websites adhering to accessibility guidelines saw increased usage and higher satisfaction ratings among all users, not just those with disabilities. Moreover, the World Health Organization emphasizes the role of accessible communication in public health campaigns, noting that inclusivity in public speaking for posters or designs can lead to more equitable outcomes.
The importance of accessibility in communication and design cannot be overstated. By adopting accessible practices, communicators and designers not only adhere to ethical and legal standards but also ensure their messages are impactful and meaningful to the widest possible audience. This commitment to inclusivity enhances the reach and effectiveness of communications across all platforms and formats.
How Accessible is Your Design?
Feedback Mechanisms to Understand Audience Better

Introduction to Feedback Mechanisms
Feedback mechanisms are essential tools for gauging audience engagement and the effectiveness of communication in formats like presentations and visual communication for posters. Whether it's a research poster narrative, an academic lecture, or a marketing campaign, understanding how your message is received allows you to make necessary adjustments to enhance clarity, engagement, and impact. These mechanisms can range from digital analytics and surveys to interactive Q&A sessions, offering valuable insights into the audience's needs and preferences.
The Role of Feedback in Communication
Feedback serves as a critical bridge between the sender and the receiver of the message, facilitating a two-way communication process that enhances understanding and engagement. When delivering public speaking for posters, for instance, feedback from the audience can help identify areas that require more clarity, topics that interest the audience the most, and the effectiveness of the chosen delivery method. For digital posters, analytics and user comments provide real-time insights into how the content is consumed and perceived, offering valuable feedback on how visual aid design for posters can be improved.
Implementing Effective Feedback Channels
Real-world examples of effective feedback mechanisms include live polling during presentations to gauge audience interest and understanding, post-event surveys for conferences and workshops, and comment sections on digital platforms that allow for direct audience interaction. In academic settings, feedback can take the form of student evaluations, which provide insights into the effectiveness of teaching methods and materials. In marketing, customer reviews and social media engagement metrics offer direct feedback on campaign performance.
Research and Insights on Feedback's Impact
Research highlights the value of feedback in improving communication outcomes. A study in the "Journal of Business and Technical Communication" found that presentations adjusted based on audience feedback were significantly more effective in achieving their objectives. Additionally, a report by the Nielsen Norman Group on user experience emphasized that websites and digital content designed with user feedback are more user-friendly and engaging. These studies underscore the importance of incorporating audience feedback to refine and enhance communication strategies.
Feedback mechanisms are indispensable for understanding and engaging your audience effectively. They provide critical insights that can be used to tailor content, improve delivery, and ensure that communication is both impactful and relevant. By prioritizing feedback, communicators can foster a deeper connection with their audience, enhancing the overall effectiveness of their message.
Anticipating Audience Questions

Introduction to Proactive Engagement
Proactively addressing audience questions is about understanding your audience's needs and concerns so deeply that you can anticipate their inquiries before they even ask. Whether you're crafting research poster narratives or delivering a business presentation, anticipating audience questions allows you to craft a message that is both informative and reassuring. By considering common questions in advance, you demonstrate thorough preparation, which strengthens trust and credibility with your audience during public speaking for posters.
Understanding Your Audience's Perspective
The key to anticipating audience questions lies in a deep understanding of your audience's background, expectations, and potential knowledge gaps. This applies equally to visual aid design for posters, where you may need to consider whether the visuals are clear, concise, and aligned with audience expectations.
Strategies for Integrating Answers
Integrating anticipated questions and their answers into your communication can be achieved in various ways. One method is to weave answers into the narrative of your presentation or document, addressing potential questions before they arise. Another approach is to include a dedicated Q&A section at the end of your presentation or document, where you explicitly address common or critical questions you expect from your audience. For digital content, FAQs or interactive elements like chatbots can serve a similar purpose, providing instant answers to common inquiries.
Evidence of Effectiveness
Research supports the effectiveness of anticipating audience questions in enhancing communication. A study in the "Journal of Psychology and Marketing" found that sales presentations addressing potential customer questions upfront were more likely to result in a sale compared to those that did not. Additionally, educational research indicates that lectures and materials that preemptively answer common student questions improve learning outcomes and student satisfaction.
Anticipating and addressing audience questions is not just about avoiding interruptions or filling content gaps; it's a proactive strategy to enhance audience engagement, satisfaction, and understanding. By thoroughly understanding your audience and integrating their potential inquiries into your message, you can easily create more effective and resonant communications.
Stay Ahead with INK PPT’s Design Trends and Insights
Integrating SEO Strategies and Keywords in Audience Engagement

Leveraging SEO for Enhanced Reach and Engagement
In the digital age, visual communication for posters is only part of the equation. Ensuring that your content is discoverable by your intended audience requires a strategic approach to SEO. By carefully integrating keywords such as crafting research poster narratives, engaging visuals for posters, and public speaking for posters into your content, you can significantly improve your content's visibility and accessibility online.
SEO: Beyond Keyword Integration
Effective SEO strategy extends beyond merely inserting keywords into your content. It involves understanding the search intent behind these keywords and crafting your content to meet these needs comprehensively. For instance, when incorporating terms like "presentation examples" or "business presentation," ensure that the content provides valuable insights, tips, or examples that users are likely to search for. Additionally, optimizing other elements such as meta descriptions, image alt texts (with phrases like "informative poster template" or "engaging presentation slides"), and internal linking structures further enhances your SEO efforts, making your content more discoverable and engaging.
Adapting Content to Evolving SEO Trends
SEO is an ever-evolving field, with search algorithms constantly updating to prioritize high-quality, relevant content. Staying informed about these changes and how they affect content discovery is crucial. For instance, the growing emphasis on user experience signals and mobile optimization reflects the need to design content that is not only informative but also accessible and user-friendly across devices. Engaging with SEO communities, attending webinars, and leveraging analytics tools are practical steps to stay ahead in the SEO game, ensuring your website and content continues to perform well in search rankings.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world examples abound of content creators and marketers who have successfully leveraged SEO to enhance audience engagement. Case studies often highlight the importance of a well-rounded SEO strategy that includes thorough keyword research, content optimization, and performance analysis. Success stories from various domains, from academic publishing to corporate marketing, demonstrate the tangible benefits of aligning content strategy with SEO best practices, resulting in increased visibility, engagement, and, ultimately, impact.
Incorporating SEO strategies into your content creation process is an essential step in ensuring that your efforts to understand and engage your audience achieve their full potential. By prioritizing SEO, you not only enhance the reach of your message but also ensure that it resonates with and is accessible to the audience you've worked so diligently to understand and connect with.
Tailor-Made Visual Solutions for Every Audience
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I make my own poster?
To make your own poster, start by defining your audience and message. Use a design tool or platform that offers an "informative poster template" to simplify the process. Incorporate engaging visuals, concise text, and ensure your design aligns with your audience's preferences and needs. Remember to utilize colors and fonts that enhance readability and attract attention.
What are the steps to create a poster?
Identify your target audience and key message.
Choose a visually appealing layout and color scheme.
Include photos engaging images or graphics relevant to your message.
Use concise, impactful text and headlines.
Incorporate feedback and revise as necessary.
How to create a poster in Word?
Open Microsoft Word and select a new blank document.
Go to the "Design" tab to set your page layout and orientation.
Use the "Insert" menu to add text boxes, images, and other visual elements.
Customize your text and images to convey your message effectively.
Print or export your poster as needed.
What is the best free online poster maker?
Canva is highly recommended for its user-friendly interface and a wide range of templates, including "informative poster templates." It offers extensive customization options, making it easy to design posters for various purposes and audiences.
How do you make a perfect poster?
A perfect poster effectively communicates its message through a balance of engaging visuals and concise text. Understand your audience's interests and preferences, choose a clear and readable font, use high-contrast colors for readability, and ensure the information is well-organized.
How do you make a good quality poster?
Focus on high-quality visuals and clarity of message. Use professional design software or online tools that offer templates designed for quality output. Pay attention to resolution and printing specifications to ensure your final product is of high quality.
What are 6 important things that must be on a poster?
Headline: Catchy and clear.
Audience-specific message: Tailored content that resonates.
Visual elements: High-quality images or graphics.
Legible fonts: Easy to read from a distance.
Contact information or call to action: What to do next.
Branding: Logos or colors that identify the presenter or organization.
How do you structure a good poster?
Begin with a powerful headline, followed by a brief introduction. Use bullet points or short paragraphs to present key information. Include visuals to support your message, and end next presentation with a clear call to action or conclusion.
How do you make a school poster look good?
Use vibrant colors and fun fonts appropriate for the school context. Include engaging, slide layout and visuals related to the topic and organize the content in an easy-to-follow manner. Incorporate elements like "engaging presentation slides" to make educational content more interesting.
What are the 5 things that make a good poster?
Clarity: Clear message and purpose.
Simplicity: Avoid clutter and focus on the key message.
Visual Appeal: Use colors, fonts, and images effectively.
Audience Engagement: Tailor the content to the audience's interests.
Actionable: Include a clear call to action.



%20(1).jpg)
%20(1).jpg)


